Table of Contents
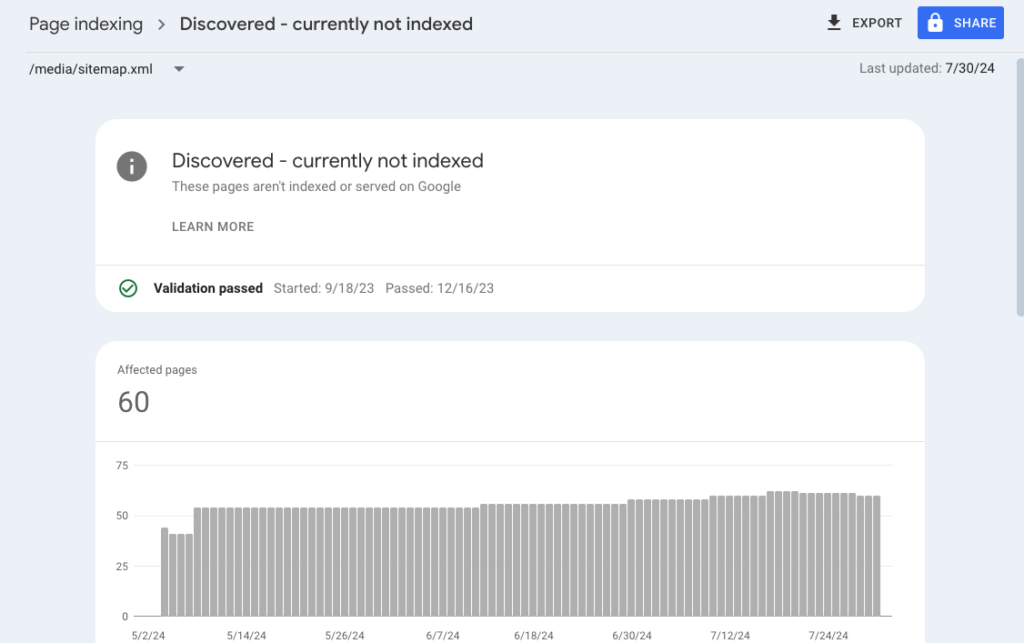
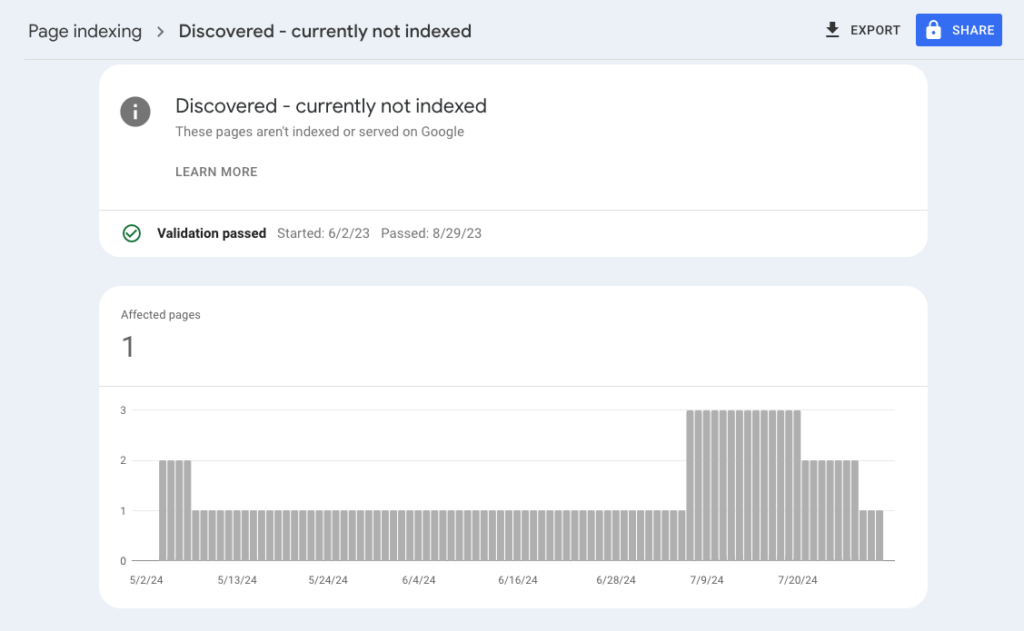
When you’re working on optimizing your website for search engines, nothing can be more frustrating than seeing the “Discovered – currently not indexed” status in Google Search Console.
This status means that Google has found your page but hasn’t yet crawled or indexed it. It’s a common issue that can affect your site’s visibility in search results.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore why this happens and provide a detailed, step-by-step approach to fix it.
Understanding “Discovered – Currently Not Indexed”
What Does “Discovered – Currently Not Indexed” Mean?
When Googlebot discovers a new URL on your site, it adds the URL to its crawl queue. However, just because a URL is in the queue doesn’t mean it will be crawled and indexed immediately.
The “Discovered – currently not indexed” status indicates that Google knows about the URL but hasn’t yet decided to crawl it.
This can happen for several reasons, including site architecture issues, crawl budget limitations, or content quality concerns.
Why is Indexing Important?
Indexing is crucial because if your pages aren’t indexed, they won’t appear in Google’s search results. This means your potential audience won’t be able to find your content, which can significantly impact your site’s traffic and overall performance.
Reasons for “Discovered – Currently Not Indexed”
Crawl Budget Limitations
Google allocates a crawl budget to each site, which is the number of pages Googlebot will crawl during a specific period.
If your site has a large number of pages or if Googlebot encounters issues while crawling, some pages may remain undiscovered or unindexed.
Low-Quality Content
Pages with thin or low-quality content may be deprioritized by Google. If your content doesn’t provide value to users, Google might decide it’s not worth indexing.
Duplicate Content
If Google detects duplicate content on your site, it may choose to index only the canonical version. Duplicate content can cause other versions of the page to be marked as “Discovered – currently not indexed.”
Technical Issues
Technical issues such as server errors, incorrect use of robots.txt, or issues with your XML sitemap can prevent Google from crawling and indexing your pages effectively.
Insufficient Internal Linking
Internal links help Googlebot discover and navigate your site. If your pages aren’t well-linked internally, they might remain undiscovered.
How to Fix “Discovered – Currently Not Indexed” Issues
Step 1: Optimize Your Crawl Budget
1. Identify Crawl Budget Issues
Use Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats report to identify any crawl budget issues. This report shows how often Googlebot crawls your site and if there are any crawling errors.
1. Improve Site Speed
A faster site can be crawled more efficiently. Optimize your site’s speed by compressing images, using a content delivery network (CDN), and minimizing JavaScript and CSS files.
1. Consolidate Duplicate Content
Use canonical tags to consolidate duplicate content and ensure that Google indexes the most relevant pages. Implement 301 redirects for redundant pages.
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/preferred-page” />
Step 2: Enhance Content Quality
1. Provide Valuable Content
Create high-quality, valuable content that answers users’ queries. Focus on providing in-depth information, using relevant keywords naturally, and ensuring your content is unique and engaging.
2. Avoid Thin Content
Ensure that all pages on your site have substantial content. Pages with little to no content may be ignored by Google. Aim for at least 300 words per page, but more importantly, ensure the content is useful and relevant.
Step 3: Fix Technical Issues
3. Check Your Robots.txt File
Ensure your robots.txt file isn’t blocking important pages from being crawled. Your robots.txt file should look something like this:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Allow: /
3. Resolve Server Errors
Use tools like Google Search Console and server logs to identify and fix any server errors (e.g., 5xx errors) that might prevent Google from crawling your site.
3. Submit an Accurate XML Sitemap
Make sure your XML sitemap is up-to-date and only includes URLs you want Google to index. Submit your sitemap through Google Search Console.
Step 4: Improve Internal Linking
4. Audit Your Internal Links
Perform an internal link audit to ensure that all important pages are well-linked from other parts of your site. Tools like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog can help you identify pages with few or no internal links.
4. Use Contextual Linking
Use contextual linking to connect related pages. This not only helps users navigate your site but also assists Google in discovering new pages.
Step 5: Use Google Search Console
5. Inspect URLs
Use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to check the status of your URLs. This tool provides insights into how Google sees your pages and can help identify issues that need fixing.
5. Request Indexing
If you’ve fixed issues on a page, use the URL Inspection tool to request indexing. This can speed up the process of getting your pages crawled and indexed.
Step 6: Regularly Monitor Your Site
6. Perform Regular Audits
Regularly audit your site to identify and fix issues before they become significant problems. Use tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and third-party SEO tools to stay on top of your site’s performance.
6. Keep Content Fresh
Regularly update your content to keep it fresh and relevant. Google favors updated content, and this can help improve your chances of getting indexed.
FAQs and Answers On Discovered – currently not indexed
What does “Discovered – currently not indexed” mean?
“Discovered – currently not indexed” is a status in Google Search Console that indicates Google has found your URL but has not yet indexed it. This means that Google is aware of the page’s existence, but it hasn’t been added to the search index, so it won’t appear in search results.
How can I check if my pages are indexed by Google?
Use the “site:” search operator in Google. For example, type site:yourdomain.com in the Google search bar to see which pages are indexed. Additionally, use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console.
How can I improve my crawl budget?
You can improve your crawl budget by optimizing your site speed, fixing crawl errors, using canonical tags, and ensuring your site structure is clean and efficient. Regularly update your XML sitemap and ensure it only includes URLs you want indexed.
Why is my high-quality content not getting indexed?
Even high-quality content can remain unindexed if there are technical issues, insufficient internal linking, or if your crawl budget is being exhausted on other pages. Make sure to audit your site for any such issues.
How long does it take for Google to index my pages?
Indexing times can vary. It can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks for Google to index your pages. Regularly update your sitemap, ensure your pages are valuable and unique, and use the URL Inspection tool to request indexing for faster results.
Real-World Example
Scenario: A Blogging Website
Imagine you run a blogging website with a mix of long-form articles, listicles, and tutorials. You notice that some of your new posts have the “Discovered – currently not indexed” status.
Here’s how you can address this issue step-by-step.
Step-by-Step Solution:
- Review Crawl Stats: Use Google Search Console to check your crawl stats. Identify any patterns or issues, such as frequent crawl errors or slow page loading times.
- Enhance Content Quality: Ensure each blog post is at least 1,000 words or check the competitors what kind of content and what’s the word count of content is they are providing and then provides unique, valuable insights. Avoid thin content and duplicate topics.
- Optimize Internal Links: Ensure every new post is linked from at least one other page on your site. Use contextual links within your articles to connect related posts.
- Check Robots.txt and Sitemaps: Ensure your robots.txt file isn’t blocking new posts. Update your XML sitemap to include all new posts and submit it to Google Search Console.
- Request Indexing: Use the URL Inspection tool to request indexing for new posts. This can speed up the process of getting your content indexed.
- Monitor Regularly: Regularly check the indexing status of your new posts. Perform monthly audits to identify and fix any recurring issues.
Conclusion
Fixing the “Discovered – currently not indexed” issue requires a comprehensive approach. By optimizing your crawl budget, enhancing content quality, resolving technical issues, and improving internal linking, you can guide Google to crawl and index your pages more effectively.
Regular monitoring and updates are crucial to maintaining a healthy SEO strategy for your website.
I’ve seen how addressing these issues can significantly improve your site’s visibility and performance in search results.
By taking a proactive and systematic approach, you can overcome indexing challenges and ensure that your content reaches its intended audience.
Additional Tips
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest SEO best practices and Google algorithm updates.
- Use SEO Tools: Utilize SEO tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz to monitor your site’s performance and identify issues early.
- Engage with the Community: Join SEO forums and communities to share experiences and learn from others facing similar challenges.
Final Thoughts
Indexing issues can be daunting, but with a clear understanding and systematic approach, they can be resolved effectively. The key is to maintain consistency, provide high-quality content, and regularly monitor your site’s performance.
By doing so, you can ensure that Google indexes your pages promptly and ranks your site higher in search results. Happy optimizing!
Need Help or Need SEO Services? Hit the button below and schedule a meeting.